ReplicableValue#
- class impacthpc.src.core.ReplicableValue(name: str | None, value: Quantity | str, min: Quantity | str | None, max: Quantity | str | None, standard_deviation: Quantity | str | None = None, warnings: List[str] = [], explaination: str | None = None, ontology: Ontology | None = None, important: bool = False)#
Bases:
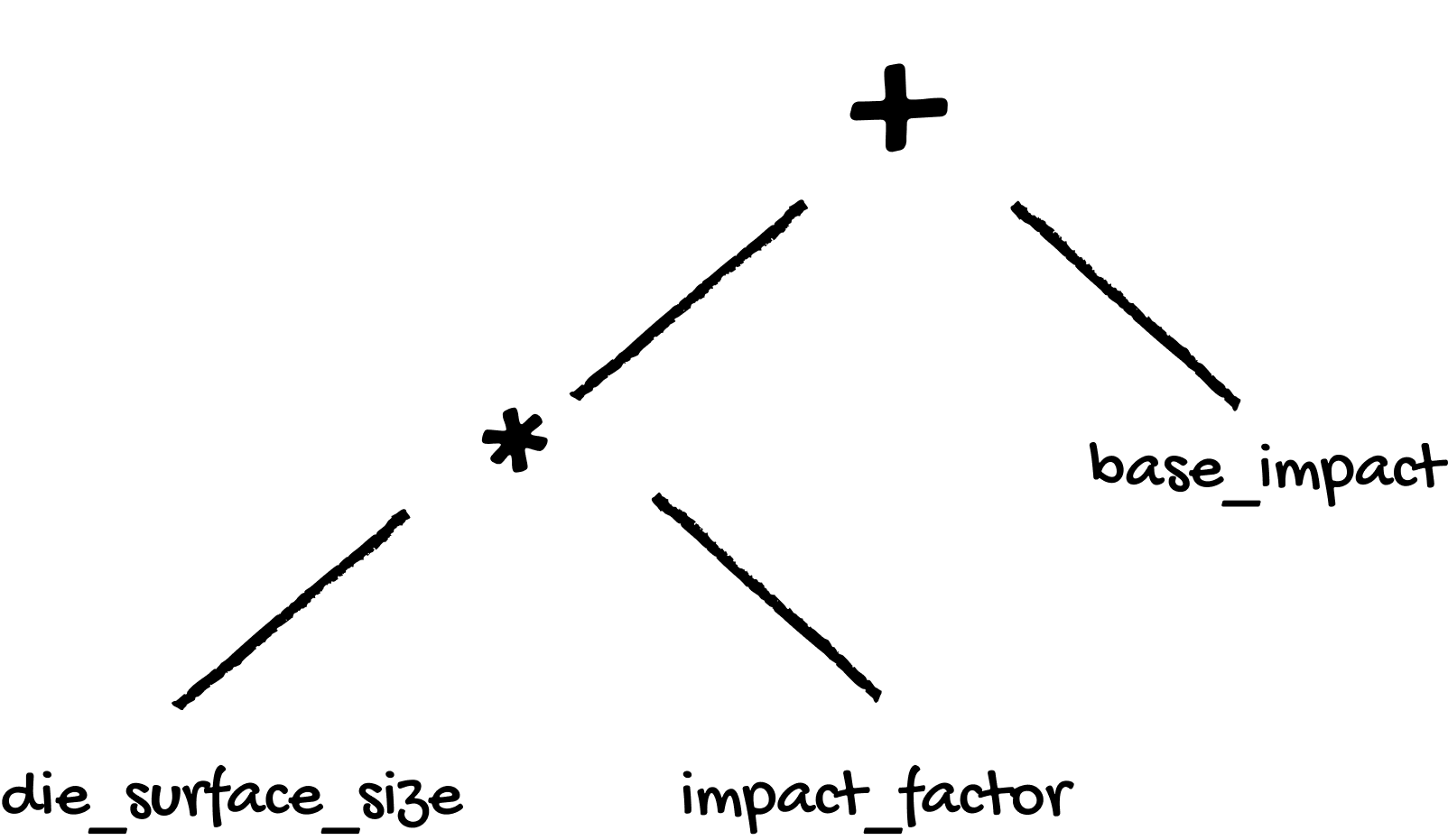
ABCReplicableValue is a core class of ImpactHPC for representing numerical values with associated uncertainties and provenance. This class enables the construction of operation trees, where each leaf represents a value (with its minimum, maximum, and standard deviation) and each node represents an operation that produces a result. Arithmetic operations between ReplicableValue instances automatically propagate uncertainties according to standard rules (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Propagation_of_uncertainty#Example_formulae). See ReplicableValue.
- correlation_mode#
(static) Class-level setting for how uncertainties are combined during operations.
- Type:
- value#
The central value, with units.
- Type:
Quantity
- min#
Minimum plausible value.
- Type:
Quantity
- max#
Maximum plausible value.
- Type:
Quantity
- standard_deviation#
Standard deviation (uncertainty) of the value.
- Type:
Quantity
- important#
True if the value is important. When true, this value is extracted during the explaination process in
explain()- Type:
Note
This class is abstract and should not be instantiated directly. Subclasses must implement
_as_formula()andexplain(). The two subclasses areSourcedValueandOperation.Attributes Summary
correlation_modeMethods Summary
average(values, unit, name, source)Computes the average of the list as a SourcedValue.
explain([formatter])Provides an explanation of the current object using the specified formatter.
ln(value)Computes the natural logarithm of a value.
make_intermediate_result(name[, ...])Makes this value an intermediate result.
set_correlation_mode(mode)Context manager to temporarily set the correlation mode used for arithmetic operations involving ReplicableValue instances.
set_unit(unit)Sets the unit of the value.
sum(values)Computes the sum of a list of ReplicableValue using
__add__(), handling duplicates.Attributes Documentation
- correlation_mode: CorrelationMode = 'INDEPENDENT'#
Methods Documentation
- static average(values: List[float | int], unit: str, name: str, source: str) SourcedValue#
Computes the average of the list as a SourcedValue.
valueis the average ofvalues.minandmaxare the minimum and maximum ofvalues.standard_deviationis the standard deviation ofvalues.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
An object containing the average, minimum, maximum, and standard deviation of the input values, all formatted with the specified unit, along with the provided name and source.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – If the input list of values is empty.
- explain(formatter: ~impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[~typing.Any, T] = <impacthpc.src.core.formatters.TextFormatter object>) T#
Provides an explanation of the current object using the specified formatter.
Internally calls
_explain_rec()and format the result withFormatter.format_result(). It extracts the important values usingextract_important_values()and pass them toFormatter.format_result().- Parameters:
formatter (impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[T]) – The formatter used to format the explanation. Defaults to
TextFormatter.recursion_level (int, optional) – The current recursion depth, used to control nested explanations. Defaults to 0.
- Returns:
The formatted explanation of the object.
- Return type:
T
- static ln(value: ReplicableValue) ReplicableValue#
Computes the natural logarithm of a value.
- Parameters:
value (ReplicableValue) – The value for which to compute the natural logarithm.
- Returns:
The result of the natural logarithm as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- make_intermediate_result(name: str, explaination: str | None = None, ontology: Ontology | None = None, override_unit: Unit | None = None)#
Makes this value an intermediate result. This is used in the explain() method. For example, if you have the computation
A + B + Cthat isn’t easy to understand, you can decompose it with intermediate results by doing:AandB = A + B AandB.make_intermediate_result("AandB") result = AandB + C result.make_intermediate_result("result")This will print something like:
result is [some_value] Formula = AandB + C where - AandB is [other value] Formula = A + B where - A is [value] - B is [value] - C is [value]You can also add an explanation and an ontology to the results, and override its unit.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the intermediate result that will be displayed by
explain().explanation (str | None, optional) – If not None, sets the
explanationattribute. Defaults to None.ontology (str | None, optional) – If not None, sets the
ontologyattribute. Defaults to None.override_unit (Unit | None, optional) – If not None, overrides the unit of the result by calling
set_unit(). Defaults to None.
- static set_correlation_mode(mode: CorrelationMode)#
Context manager to temporarily set the correlation mode used for arithmetic operations involving ReplicableValue instances. ReplicableValue instances represent random variables, where the value attribute is the expectation and the standard_deviation attribute quantifies uncertainty. When performing arithmetic operations on these values, the standard deviation of the result depends on the correlation between operands. In practice, determining the exact correlation between arbitrary values is often infeasible.
To address this, ImpactHPC restricts correlation handling to two modes: - Independent (correlation = 0): Standard deviations are combined assuming no correlation. - Dependent (correlation = 1): Standard deviations are combined assuming full positive correlation.
This context manager allows you to specify which correlation mode should be used within a given block of code. For example, when subtracting a value from itself (e.g., C - C), the operands are fully correlated, and the standard deviation of the result should be zero. In contrast, when adding unrelated values (e.g., A + B), the operands are considered independent.
Example usage: .. code-block:: python
- with ReplicableValue.set_correlation_mode(CorrelationMode.DEPENDENT):
# Computations here assume full correlation (correlation = 1) result = C - C
# Outside the context, computations assume independence (correlation = 0) result2 = A + B
This approach simplifies the handling of correlations in complex systems, such as server impact computations, by allowing explicit control over correlation assumptions at the group or component level.
- Parameters:
mode (CorrelationMode) – The correlation mode to use within the context.
- set_unit(unit: Unit)#
Sets the unit of the value. ImpactHPC uses the library Pint (https://pint.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) for handling units.
- Parameters:
unit (Unit) – The new unit. You should use a Unit from
impacthpc.src.core.config.ureg.- Raises:
ValueError – Raised if the value should be dimensionless to be set but is not.
- static sum(values: List[ReplicableValue]) ReplicableValue#
Computes the sum of a list of ReplicableValue using
__add__(), handling duplicates. Duplicates are removed:same_value + other_value + same_value + same_valuebecomesother_value + 3 * same_value.- Parameters:
values (List[ReplicableValue]) – The list to sum.
- Returns:
The sum of the ReplicableValue instances in
values.- Return type:
- __add__(other: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
- __mul__(other: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
- __sub__(other: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
- __truediv__(other: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
- static _add(a: ReplicableValue | int | float, b: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
Implements the addition operator for ReplicableValue objects. Supports addition with another ReplicableValue, int, or float. If
otheris an int or float, the value is added to the current value, considering a standard deviation of 0 and the same unit as self.- Parameters:
a (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The first operand
b (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The second operand
- Returns:
The result of the addition as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- abstractmethod _as_formula() str#
Returns a string representing the formula that this ReplicableValue represents.
- static _div(a: ReplicableValue | int | float, b: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
Implements the division operator for ReplicableValue objects. Supports division with another ReplicableValue, int, or float. If
otheris an int or float, the value is added to the current value, considering a standard deviation of 0 and the same unit as self.- Parameters:
a (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The first operand
b (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The second operand
- Returns:
The result of the division as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- abstractmethod _explain_rec(formatter: ~impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[~typing.Any, T] = <impacthpc.src.core.formatters.TextFormatter object>, recursion_level: int = 0, already_seen_values: set[int] = {}) T | list[T]#
Recusive method called by
explain()to provides an explanation of the current object using the specified formatter.- See implementations in:
- Args:static_usage_attributed_to_job
formatter (impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[T]): The formatter used to format the explanation. Defaults to
TextFormatter. recursion_level (int, optional): The current recursion depth, used to control nested explanations. Defaults to 0. already_seen_values (set[int]): A set of hashs of theReplicableValuethat have already been traversed when a value is duplicated and present in several branches.
- Returns:
The formatted explanation of the object.
- Return type:
T
- static _mul(a: ReplicableValue | int | float, b: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
Implements the multiplication operator for ReplicableValue objects. Supports multiplication with another ReplicableValue, int, or float. If
otheris an int or float, the value is added to the current value, considering a standard deviation of 0 and the same unit as self.- Parameters:
a (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The first operand
b (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The second operand
- Returns:
The result of the multiplication as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- static _sub(a: ReplicableValue | int | float, b: ReplicableValue | int | float) ReplicableValue#
Implements the substraction operator for ReplicableValue objects. Supports substraction with another ReplicableValue, int, or float. If
otheris an int or float, the value is added to the current value, considering a standard deviation of 0 and the same unit as self.- Parameters:
a (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The first operand
b (ReplicableValue | int | float) – The second operand
- Returns:
The result of the substraction as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- static average(values: List[float | int], unit: str, name: str, source: str) SourcedValue#
Computes the average of the list as a SourcedValue.
valueis the average ofvalues.minandmaxare the minimum and maximum ofvalues.standard_deviationis the standard deviation ofvalues.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
An object containing the average, minimum, maximum, and standard deviation of the input values, all formatted with the specified unit, along with the provided name and source.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – If the input list of values is empty.
- correlation_mode: CorrelationMode = 'INDEPENDENT'#
- explain(formatter: ~impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[~typing.Any, T] = <impacthpc.src.core.formatters.TextFormatter object>) T#
Provides an explanation of the current object using the specified formatter.
Internally calls
_explain_rec()and format the result withFormatter.format_result(). It extracts the important values usingextract_important_values()and pass them toFormatter.format_result().- Parameters:
formatter (impacthpc.src.core.formatters.Formatter[T]) – The formatter used to format the explanation. Defaults to
TextFormatter.recursion_level (int, optional) – The current recursion depth, used to control nested explanations. Defaults to 0.
- Returns:
The formatted explanation of the object.
- Return type:
T
- static ln(value: ReplicableValue) ReplicableValue#
Computes the natural logarithm of a value.
- Parameters:
value (ReplicableValue) – The value for which to compute the natural logarithm.
- Returns:
The result of the natural logarithm as a new Operation object.
- Return type:
- Raises:
NotImplementedError – If the operand type is not supported.
- make_intermediate_result(name: str, explaination: str | None = None, ontology: Ontology | None = None, override_unit: Unit | None = None)#
Makes this value an intermediate result. This is used in the explain() method. For example, if you have the computation
A + B + Cthat isn’t easy to understand, you can decompose it with intermediate results by doing:AandB = A + B AandB.make_intermediate_result("AandB") result = AandB + C result.make_intermediate_result("result")This will print something like:
result is [some_value] Formula = AandB + C where - AandB is [other value] Formula = A + B where - A is [value] - B is [value] - C is [value]You can also add an explanation and an ontology to the results, and override its unit.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the intermediate result that will be displayed by
explain().explanation (str | None, optional) – If not None, sets the
explanationattribute. Defaults to None.ontology (str | None, optional) – If not None, sets the
ontologyattribute. Defaults to None.override_unit (Unit | None, optional) – If not None, overrides the unit of the result by calling
set_unit(). Defaults to None.
- static set_correlation_mode(mode: CorrelationMode)#
Context manager to temporarily set the correlation mode used for arithmetic operations involving ReplicableValue instances. ReplicableValue instances represent random variables, where the value attribute is the expectation and the standard_deviation attribute quantifies uncertainty. When performing arithmetic operations on these values, the standard deviation of the result depends on the correlation between operands. In practice, determining the exact correlation between arbitrary values is often infeasible.
To address this, ImpactHPC restricts correlation handling to two modes: - Independent (correlation = 0): Standard deviations are combined assuming no correlation. - Dependent (correlation = 1): Standard deviations are combined assuming full positive correlation.
This context manager allows you to specify which correlation mode should be used within a given block of code. For example, when subtracting a value from itself (e.g., C - C), the operands are fully correlated, and the standard deviation of the result should be zero. In contrast, when adding unrelated values (e.g., A + B), the operands are considered independent.
Example usage: .. code-block:: python
- with ReplicableValue.set_correlation_mode(CorrelationMode.DEPENDENT):
# Computations here assume full correlation (correlation = 1) result = C - C
# Outside the context, computations assume independence (correlation = 0) result2 = A + B
This approach simplifies the handling of correlations in complex systems, such as server impact computations, by allowing explicit control over correlation assumptions at the group or component level.
- Parameters:
mode (CorrelationMode) – The correlation mode to use within the context.
- set_unit(unit: Unit)#
Sets the unit of the value. ImpactHPC uses the library Pint (https://pint.readthedocs.io/en/stable/) for handling units.
- Parameters:
unit (Unit) – The new unit. You should use a Unit from
impacthpc.src.core.config.ureg.- Raises:
ValueError – Raised if the value should be dimensionless to be set but is not.
- static sum(values: List[ReplicableValue]) ReplicableValue#
Computes the sum of a list of ReplicableValue using
__add__(), handling duplicates. Duplicates are removed:same_value + other_value + same_value + same_valuebecomesother_value + 3 * same_value.- Parameters:
values (List[ReplicableValue]) – The list to sum.
- Returns:
The sum of the ReplicableValue instances in
values.- Return type: